EVALUATION OF RESISTANCE TO EROSION BY CAVITATING LIQUID JET OF MATERIALS USED IN CENTRIFUGAL PUMP IMPELLERS
Abstract
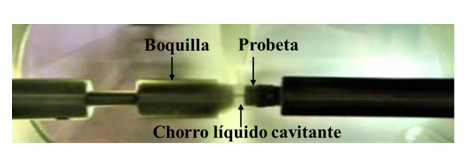
In this paper, cavitating liquid jet (water) erosion tests were performed on various materials, machined in the form of specimens, using the method established in the ASTM G-134 standard. The materials used were: stainless steels (AISI 316, AISI 410 and commercial grade 15-5 PH) and a Ni-Cu alloy (trade name Monel K500); all of these contemplated in the API 610 standard for the manufacturing of centrifugal pump impellers and additionally, a CoCr weld overlay (trade name Estelite 6). They were characterized chemically, microstructurally and mechanically. The materials were subjected to the impact of a cavitating jet emerging from a cylindrical nozzle, for stipulated and timed times, thus producing erosion in them, quantified by the loss of mass. The materials were inspected visually and microscopically, analyzing the total mass loss with respect to their hardness and also comparing the cumulative erosion rates as a function of time. It was found that Estelite 6 was the most resistant material to this type of wear, followed by AISI 410 stainless steel and its version hardened by heat treatment; grade 15-5 PH stainless steel had medium resistance; while AISI 316 stainless steel and Monel K500 showed the greatest mass losses in the test.Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The authors of papers accepted for publication by the RLMM, should recognize the complete transfer of copyright (in all languages) to the RLMM. This transfer includes the right by the RLMM to adapt the article for digital or printed reproduction without altering the written content and information displayed in tables or figures within. The authors retain the copyright and guarantee the journal the right to be the first publication of the work as well as licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Internacional (CC BY 4.0) which allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the authorship of the work and the initial publication in this journal.



